Your Read is on the Way
Every Story Matters
Every Story Matters
The Hydropower Boom in Africa: A Green Energy Revolution Africa is tapping into its immense hydropower potential, ushering in an era of renewable energy. With monumental projects like Ethiopia’s Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam (GERD) and the Inga Dams in the Democratic Republic of Congo, the continent is gearing up to address its energy demands sustainably while driving economic growth.
Northern Kenya is a region rich in resources, cultural diversity, and strategic trade potential, yet it remains underutilized in the national development agenda.

Can AI Help cure HIV AIDS in 2025

Why Ruiru is Almost Dominating Thika in 2025

Mathare Exposed! Discover Mathare-Nairobi through an immersive ground and aerial Tour- HD

Bullet Bras Evolution || Where did Bullet Bras go to?
Taxes are the backbone of Kenya’s national development. They fund roads, hospitals, schools, security, and virtually every public service. Whether you’re an individual, a company, or an importer, understanding what taxes apply to you is crucial to staying compliant and avoiding penalties.
Kenya’s tax system is primarily managed by the Kenya Revenue Authority (KRA), which oversees the collection of all taxes due under various laws.
Let’s break down the main categories of taxes in Kenya and how they apply.
Income tax is levied on gains or profits from employment, business activities, rent, investments, and pensions.
-PAYE (Pay As You Earn): Deducted by employers from salaried employees.
-Turnover Tax (TOT): For small businesses earning between KES 1M–25M per year.
-Corporation Tax: Paid by companies on profits (usually at 30% for residents, 37.5% for non-residents).
-Withholding Tax: Deducted at source from dividends, interest, royalties, and professional fees.
-Advance Tax: Paid in advance by owners of commercial vehicles before license renewal.
-Rental Income Tax: On income from residential and commercial properties.
VAT is charged on the sale of goods and services and is usually passed on to the final consumer.
-Standard rate: 16%
-Zero-rated: 0% (applies to exports and certain basic items)
-Exempt: Some goods and services (e.g., education, medical services)
Businesses with an annual turnover of over KES 5 million must register for VAT.
Excise duty is a tax on specific goods and services, particularly those considered harmful or luxurious.
-Alcoholic and sugary drinks
-Cigarettes and tobacco
-Betting and gaming services
-Motor vehicles
-Fuel products
Excise duty is intended both to raise revenue and discourage consumption of certain goods.
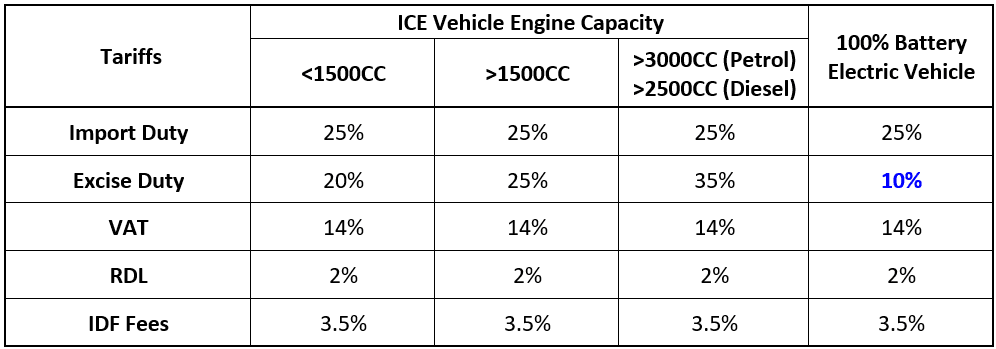
Customs duty is levied on goods imported into Kenya. The amount charged depends on the nature, quantity, and value of the goods.
-Import Duty
-Import Declaration Fee (IDF)
-Railway Development Levy (RDL)
This tax protects local industries and raises revenue from international trade.
CGT is imposed on the profit earned from the transfer (sale) of property such as land, buildings, and shares.
-Currently charged at 15% on the net gain.
-Applies only to the gain—not the total sale value.
-Payable within 30 days of property transfer.
This is charged on legal documents involved in transactions such as property transfers, leases, and company share transfers.
-4% for urban property transfers
-2% for rural property
-1% for share transfers
Stamp duty must be paid before a title or legal right is registered.
KRA also collects certain taxes and levies on behalf of other government agencies.
Examples include:
-Road Maintenance Levy
-Petroleum Development Levy
-Air Passenger Service Charge
These are often embedded in service or product costs and remitted to specific agencies.
This tax was previously charged at 15% of the single business permit fee, especially for informal sector businesses. It was replaced largely by the Turnover Tax (TOT) but may still apply under specific local authority regulations.
Kenya’s taxation framework is structured, detailed, and diversified. Whether you're a salaried worker, an entrepreneur, an investor, or an importer, there’s a tax obligation you must meet. Understanding the types of taxes and how they apply to your circumstances can save you from penalties, help you manage your finances better, and ensure that you contribute to national development responsibly.
0 comments